Industry Application: Intelligent Unmanned Operation Solutions for Lakes – Rapid Deployment for Continuous Protection
China boasts vast territory, abundant rivers and lakes, and developed water systems. Among them, there are 45,203 rivers with a drainage area of over 50 square kilometers, totaling a length of 1.5085 million kilometers. There are more than 2,865 natural lakes with an annual average water surface area of over 1 square kilometer, with a total lake water surface area of 78,000 square kilometers.
In recent years, comprehensive treatment of air, water, and soil has become a focus. Due to its close integration with daily life and industrial production, water pollution has surpassed air pollution to become the most pressing concern. According to incomplete statistics, more than 90% of urban water bodies in China suffer from varying degrees of pollution.
Water pollution manifests on the surface, originates underwater, and stems from shoreline activities. Therefore, continuous monitoring, cleaning, and remediation, coupled with shoreline pollution management, are essential to address external pollution, internal pollution, and the degradation of aquatic ecosystems. To tackle this issue, an intelligent, unmanned water operation and maintenance solution has been introduced. Recently, this solution has been implemented on a large scale in lake environments, bringing unmanned and intelligent technology into ecological construction, providing strong support for sustainable development.

Intelligent Operation and Maintenance Solution for Small Artificial Lakes:
Shenzhen Lianhuashan Park Implementation Case
Shenzhen Lianhuashan Park is located at the northernmost end of the central district of Shenzhen, Guangdong Province, covering an area of 194 hectares. It consists of a lawn area, a palm forest area, and the artificial Lianhua Lake area. Lianhuashan Park is an ecological municipal park and a scenic area where people and nature coexist harmoniously, serving as a "living museum."
Lianhua Lake covers more than 20,000 square meters, attracting many visitors and featuring long shorelines, necessitating regular water surface cleaning. Floating debris mainly consists of leaves and foam. Previously, workers relied on small boats to manually clean the lake, which was time-consuming, labor-intensive, and posed safety risks.

Media Coverage of Intelligent Water Operation and Maintenance Projects
The deployment of the SMURF unmanned cleaning boat has significantly improved the efficiency of inspection and daily cleaning operations. For safety and efficiency, unmanned charging docks were installed along the shore, away from visitor pathways. The unmanned boat autonomously returns for charging when the garbage load is full or the battery is low, ensuring continuous cleaning and full coverage protection.
Supervisor's Feedback:
"The unmanned cleaning boat performs carpet-like cleaning, collecting floating debris on the lake surface with 360-degree coverage and no blind spots. A single charge allows for six hours of continuous operation, with three cleanings per day. It is particularly effective for cleaning debris in the center of the lake, maintaining a better overall condition than four workers combined."
As a prominent feature along Shenzhen's central axis, protecting the aquatic ecosystem of Lianhua Lake is a top priority. Through the deployment of the intelligent, unmanned water operation and maintenance solution, the park's water environment has improved significantly, enhancing the living standards of nearby residents.

Autonomous Intelligent Operation and Maintenance Solution for Ecological Lakes:
Shenzhen Xianhu Botanical Garden Implementation Case
Shenzhen Xianhu Botanical Garden, located in Luohu District, Shenzhen, is centered around the lake embraced by mountains. The shoreline of Xianhu Lake is winding and dotted with islands, supporting diverse aquatic flora and fauna. The lakeside boardwalk is an essential route for plant education in the park, imposing higher ecological requirements on the water environment.
The SMURF unmanned cleaning boat removes leaves, floating silt, and foam. The team designed two cleaning routes for the boat: one for the central waterway and one for the shoreline. Equipped with unmanned charging docks, the boat operates 24/7 and prevents unauthorized contact by visitors, ensuring equipment safety.
By upgrading the water area with intelligent technology, the water ecosystem of Xianhu Botanical Garden has achieved high standards of comprehensive, all-weather, and full-range protection. Replacing hazardous manual operations with unmanned solutions reduces labor, lowers costs, and enhances efficiency, contributing to the ecological preservation of the park.
Intelligent Operation and Maintenance Solution for Urban Park Lakes:
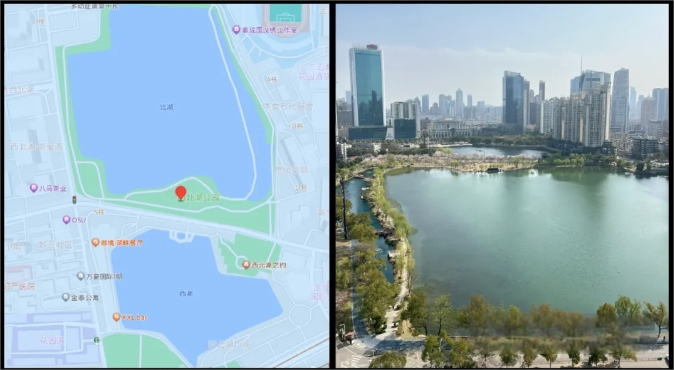
Wuhan Northwest Lake Park Implementation Case
Northwest Lake Park, located in the northern corner of Jianghan District, Wuhan, is one of the city's major urban parks. It comprises two lakes—West Lake and North Lake—with a total water area of 14.39 hectares and green space covering 24.34 hectares.
The long shoreline of North Lake often accumulates floating debris, posing challenges for manual cleaning due to the extensive area and length of cleaning routes. The SMURF unmanned boat, equipped with charging docks, operates around the clock, promptly addressing floating debris as it appears.

On-site Implementation of SMURF Unmanned Charging Docks
The intelligent, unmanned water operation and maintenance solution has significantly enhanced the ecological environment of North Lake, enabling technological, unmanned, and all-weather water surface cleaning operations.
The intelligent water operation and maintenance solution will continue to serve industry frontline workers, minimizing the risks associated with manual cleaning, freeing up labor, and achieving cost reduction and efficiency gains. Continuous technological innovation will drive the intelligent and digital transformation of water environmental protection and water management industries, safeguarding the nation's green waters and mountains.
Unmanned operations make water areas cleaner and more beautiful.
- Reinforcement Learning Enables Bipedal Robot to Conquer Challenging Terrain
- Drones for 3D Indoor Exploration-Cultural Relics Protection and Indoor Survey
- Industry Application: Intelligent Unmanned Operation Solutions for Lakes – Rapid Deployment for Continuous Protection
- High-Altitude Cleaning Case Introduction - Drone Spraying and Cleaning
- New Performance: SLAM Handheld Lidar Scanner + External Panoramic Camera New Combination